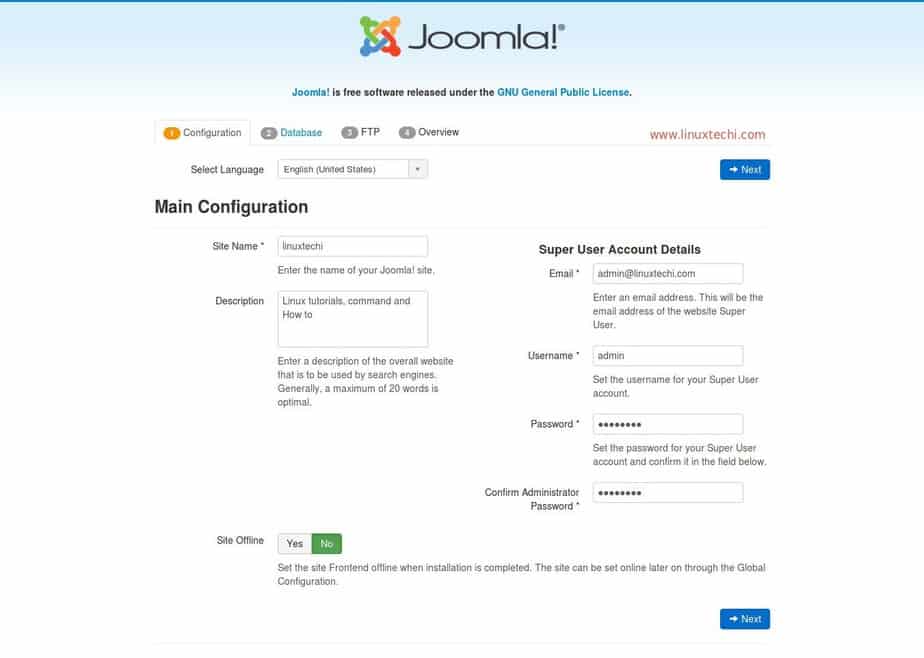
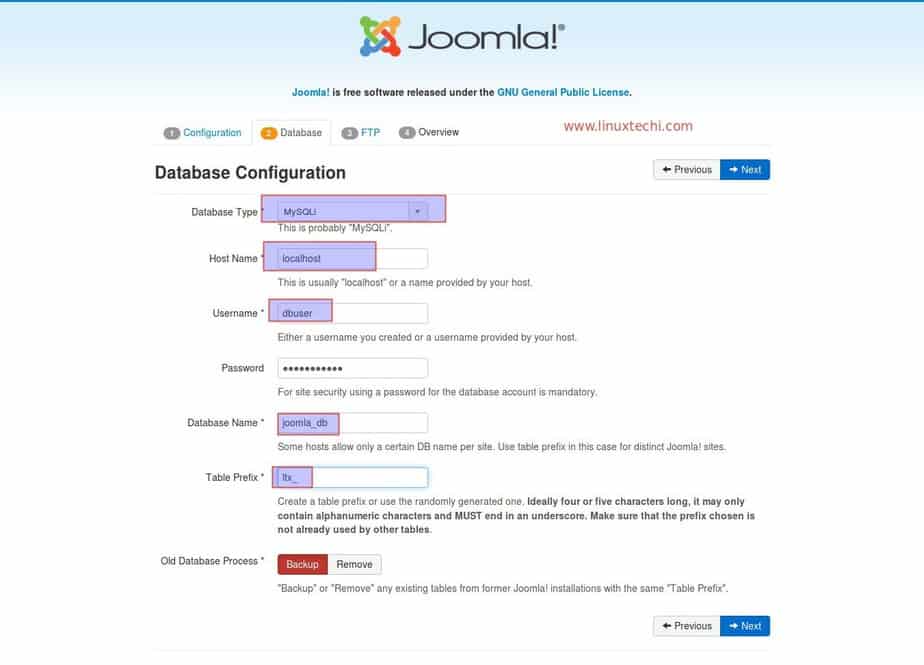
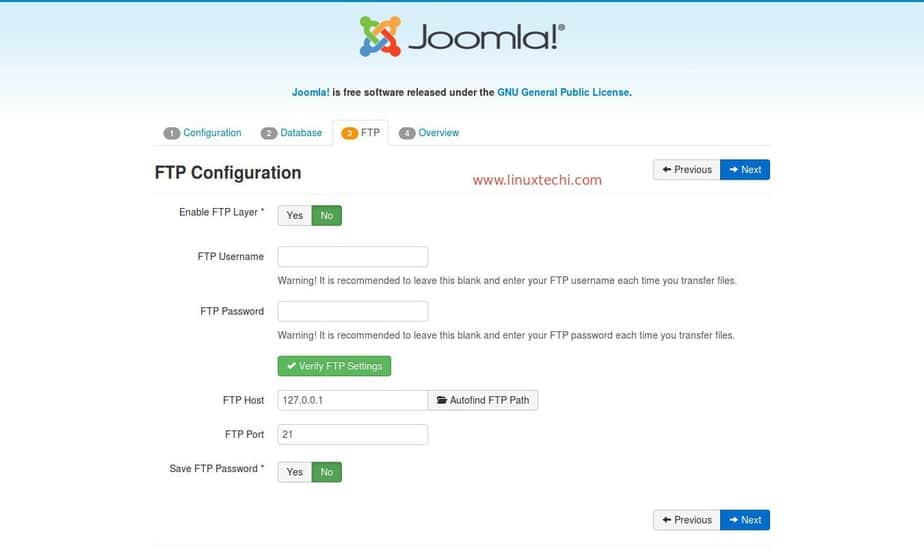
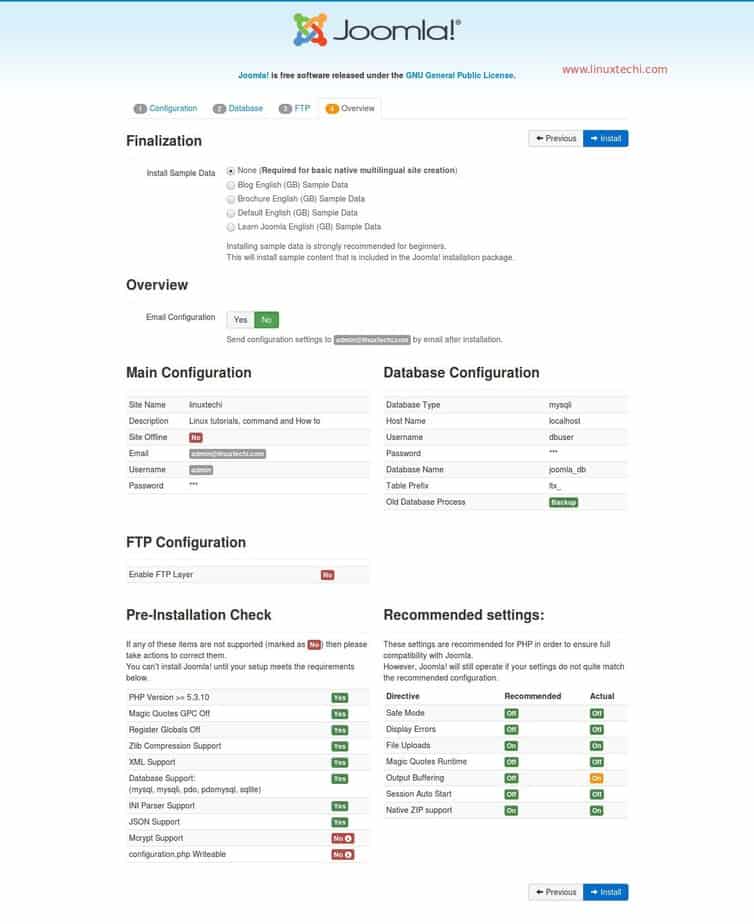
Step 1
Install required packages for couchdb for manual installation.
yum install autoconf autoconf-archive automake curl-devel help2man js-devel libicu-devel libtool perl-Test-Harness -y
if any fails then install epel install that failed dependencies.
yum install epel-release
Step 2
Download the erlang rpm package cause source is not working perfectly to me so i decide to install rpm.
wget https://packages.erlang-solutions.com/erlang/esl-erlang/FLAVOUR_1_general/esl-erlang_19.3.6-1~centos~6_amd64.rpm
now run the below command to start install.
Note: couchdb is required 20 or below erlang
rpm -Uvh esl-erlang_19.3.6-1~centos~6_amd64.rpm
Step 3
Now download couchDB from the source
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/couchdb/source/2.1.1/apache-couchdb-2.1.1.tar.gz
untar the package with following command
tar xzf apache-couchdb-2.1.1.tar.gz
after that goto that directory and start configure it.
Note: there is no need of prefix or anything else in above 2.0 version it will load the package in rel in the configuration folder.
cd apache-couchdb-2.1.1
now run the command below mention to configure.
./configure
then run make
make
and then run make release it will do the mail installation.
make release
if you face any issue on this just install couchdb with yum and try it will work.
now couchdb installed successfully. we can move the directory to any where to start.
mv apache-couchdb-2.1.1/rel/couchdb /opt
start the couchdb from bin directory with below command
./couchdb &
Step 4
If we have multiple couchdb on same server then we need to made one change vm.args in couchdb/etc location. I have mentioned it below.
# Multiple CouchDBs running on the same machine can use couchdb1@, couchdb2@,
# etc.
-name couchdb1@127.0.0.1
after that try to run the both couchdb in same server.
Step 5
For create noramal user we can use the below details.
click the users in database like screenshot below

Then click Click Document

It will show like below screenshots

and add the below details on it
Install required packages for couchdb for manual installation.
yum install autoconf autoconf-archive automake curl-devel help2man js-devel libicu-devel libtool perl-Test-Harness -y
if any fails then install epel install that failed dependencies.
yum install epel-release
Step 2
Download the erlang rpm package cause source is not working perfectly to me so i decide to install rpm.
wget https://packages.erlang-solutions.com/erlang/esl-erlang/FLAVOUR_1_general/esl-erlang_19.3.6-1~centos~6_amd64.rpm
now run the below command to start install.
Note: couchdb is required 20 or below erlang
rpm -Uvh esl-erlang_19.3.6-1~centos~6_amd64.rpm
Step 3
Now download couchDB from the source
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/couchdb/source/2.1.1/apache-couchdb-2.1.1.tar.gz
untar the package with following command
tar xzf apache-couchdb-2.1.1.tar.gz
after that goto that directory and start configure it.
Note: there is no need of prefix or anything else in above 2.0 version it will load the package in rel in the configuration folder.
cd apache-couchdb-2.1.1
now run the command below mention to configure.
./configure
then run make
make
and then run make release it will do the mail installation.
make release
if you face any issue on this just install couchdb with yum and try it will work.
now couchdb installed successfully. we can move the directory to any where to start.
mv apache-couchdb-2.1.1/rel/couchdb /opt
start the couchdb from bin directory with below command
./couchdb &
Step 4
If we have multiple couchdb on same server then we need to made one change vm.args in couchdb/etc location. I have mentioned it below.
# Multiple CouchDBs running on the same machine can use couchdb1@, couchdb2@,
# etc.
-name couchdb1@127.0.0.1
after that try to run the both couchdb in same server.
Step 5
For create noramal user we can use the below details.
click the users in database like screenshot below
Then click Click Document
It will show like below screenshots
and add the below details on it
{
"_id": "org.couchdb.user:readonly",
"name": "readonly",
"password": "readonly",
"roles": [],
"type": "user"
}
then add the users to database in permission tab.